Basic Human Eye Anatomy
Human eye is considered as one of the five sense organs. It is the most important organ of the human body as this sense organ helps human beings to see the surrounding world. Most people agree to the fact that eyes are valuable than any other sense organ. It works like a camera as it refracts light from the focused object to produce an image of the object. The retina identifies the image and sends the details to the brain with the help of the optic nerve. Thus, the eyeball helps human beings to see three-dimensional images of various objects.
Human Eye Anatomy and Eye Surgery Types
Different Parts of the Human Eye (Human Eye Anatomy)
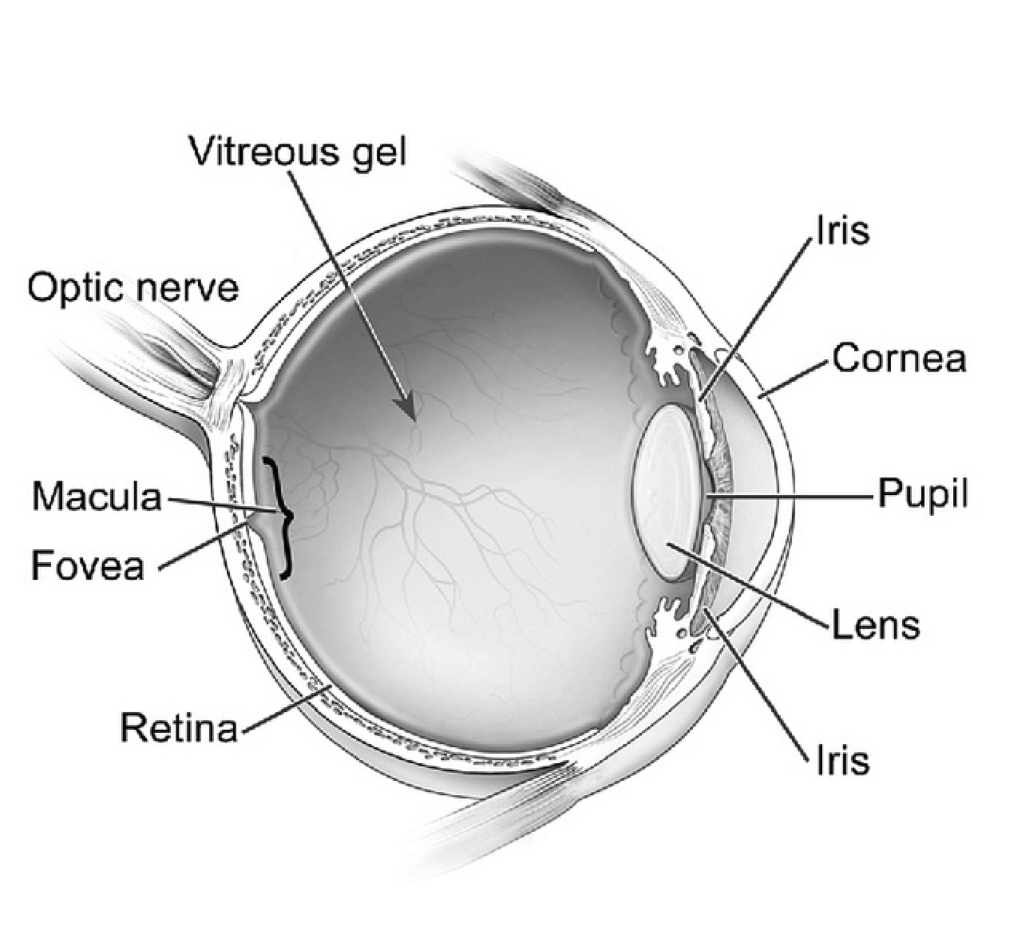
The eyeball consists of three layers:
- Cornea and sclera together form the outer layer
- Iris and pupil form the middle layer of the eyeball
- The inner layer of the eye consists of the retina
Sclera: Sclera is the outermost layer that helps to maintain the shape of the human eye. Sclera is the toughest part of the eye that provides protection and strength to the eye. The muscles of the sclera help in the movement of eyeballs.
Cornea: Cornea is transparent and allows the light to pass into the eye. It is also known as the “front window of the eye”. The refractive power of the cornea makes the light rays to bend, so that they can pass through the pupil easily. Cornea is made of 5 layers of tissues. The outer layer protects the eye and inner layers give strength to the eye.
Iris: Iris is the colored part situated between the lens and cornea. The color of the iris varies from blue, green to dark brown. The color of the pigment cells and connective tissue determines the color of the iris. If iris has more pigment, then the color of the eyes will become brown. If the pigmentation is less, then the color of the eyes will become blue. The iris controls the size of the pupil by expanding or contracting the muscles surrounding it.
Pupil: It is a black round hole located in the center of the iris. The amount of light entering into the eye is controlled by the pupil by changing its size automatically. The pupil becomes smaller or larger with the help of iris muscles.
Lens: It is a transparent tissue situated behind the iris and pupil. The lens focuses on the light rays and the light rays enter through the pupil to form an inverted image of the focused object on the retina.
Aqueous Humor: It is a watery fluid that fills the space between the iris and cornea. It provides nutrition to the cornea and shape to the eye.
Vitreous Humor: Vitreous humor is a jelly-like fluid found inside the cavity of the eye. The function of the vitreous gel is to maintain the shape of the eyeball.
Macula: It is a small sensitive area situated near the retina, which helps in seeing the objects accurately.
Fovea: It is a small pit situated in the middle of the macula, which helps the eye to get the best possible vision.
Retina: It is a multi-layered membrane found in the inner lining of the eyeball, which consists of millions of light sensitive cells such as rods and cones. The retina converts light refracted from the objects into electric impulses. The electric impulses are then send to the brain resulting in vision.
Optic Nerve: Optic nerve consists of thousands of nerve fibers and it passes the signals from the retina to the brain.
Eye surgery has progressed significantly over the past ten years.
Based on your eye condition, you have several options for surgery.
If your condition is simply vision correction, then you will need to evaluate LASIK vision correction services.
If you have difficulty seeing, like having a yellow piece of wax paper in your eye, or very cloudy vision, you may have cataracts. Cataracts typically require surgery, where your lens will be replaced with an artificial lens. Cataract outpatient surgery is a common type of surgery, that has been refined over the past five years. However, are still opportunities for complications, so make sure you do your research on your surgeon and the procedure that will best meet your vision correction needs.
A more serious eye condition is Glaucoma, which if left untreated can cause blindness. Glaucoma is a condition where there is gradual damage to your optic nerve, typically later in life. There are eye drops and surgical procedures now available for Glaucoma. These surgical procedures include laser and conventional surgery. Doing your research will be important as new medications have made eye drops very effective treatment option. Because people have very few symptoms of glaucoma it is important to have an annual eye exam to check the pressure in your eyes and determine if you have early signs of Glaucoma.
For additional information:
Evolution and Types of Eye Surgery
LASIK Success Factors
LASIK
Cataract Surgery – Choosing a surgeon
Cataract Surgery-Risks
Glaucoma Introduction and Description
Glaucoma Symptoms