Heart Surgeon
A cardiovascular surgeon is commonly called a heart surgeon; the most common heart surgery they perform is bypass surgery, also called CABG (coronary artery bypass graft). The image shown to the left is 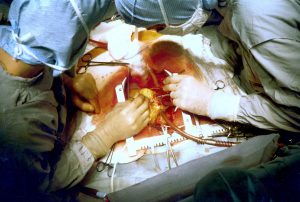 of a CABG surgery. They also do stents, pacemakers, and open heart surgery for heart valve repairs, and valve replacements. And when the heart fails, they can transplant a new one.
of a CABG surgery. They also do stents, pacemakers, and open heart surgery for heart valve repairs, and valve replacements. And when the heart fails, they can transplant a new one.
Cardio-thoracic Surgery
Cardio-thoracic surgery is the field of medicine involved in surgical treatment of diseases and disorders that affect organs inside the chest—the heart (heart disease) and lungs (lung disease). They also perform operations on blood vessels in your body, including the aorta—which is the body’s main supplier of blood.
Cardiovascular Surgeries, Procedures and Operations
Cardiovascular surgeons perform many different types of operations. Below is an alphabetical list of surgeries performed by a cardiovascular (and cardio-thoracic) surgeon.
Aneurysm Repair
- An aneurysm may occur when a blood vessel wall weakens and then bulges (balloons) as a result of the pressure of blood flowing into the weakened area. As this is a blood vessel related condition, a cardiovascular surgeon is called upon to repair an aneurysm (If the aneurysm is located in the brain however, a neurosurgeon may be used.)
Carotid Artery Endarterectomy
- Plaque, fat or waxy build up in the carotid artery (blood vessel) is a condition otherwise known as Carotid Artery Disease. If not treated it can cause a stroke. Carotid Artery Endarterectomy is a procedure (performed by vascular surgeons or neurosurgeons) to remove this plaque, fat or waxy build up.
Coronary Artery Bypass Graft
- Coronary Artery Bypass Graft, or more often referred to by its acronym CABG (pronounced ‘cabbage’), is a procedure where blood flow is restored to an area of the heart where it has previously been blocked. Blood flow can become blocked to an area of the heart when Coronary Artery Disease is present. A vein from a patient’s arm, chest or leg may be used as a new vein to shunt blood to the blocked area.
- This is major, open-heart surgery, where the chest is cut down the center rib cage and opened up to access the heart. The surgery takes about three to six hours and is performed under general anesthesia.
Defibrillator Implant
- People who suffer from different cardiac arrhythmias (irregular heart beats), who have an abnormal muscle condition of the heart muscle, or who have had a heart attack with heart damage, may be recommended to get a defibrillator implant.
- The more common type of implant is called an Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator (ICD). It is a small square-shaped device that is implanted under the left collarbone, under the skin. If the ventricles of the heart begin to beat irregularly the defibrillator device can give the heart a “jump start” and put it back into a regular rhythm.
Ductus Arteriosus Closure
- After birth infants can develop a heart problem called Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA). In normal birth transition the duct goes from being patent to closed. In this heart condition the duct remains patent and can be life threatening. This condition can be treated with medications, catheter based procedures or surgery. When surgery is needed a cardiovascular surgeon is called upon (they would likely also be specialized in pediatrics).
Endovascular Surgery
- Endovascular surgery is a surgical technique that allows for the treatment and repair of varying blood vessel conditions. The technique is considered less invasive and is accomplished by inserting catheters (and/or other required tools) through a large vein near the hip bone to access the affected vessel.
Heart Transplant and Heart-Lung Transplant
- Cardiovascular surgeons may also perform heart transplant or heart-lung transplant surgeries.
- Heart transplant is when a donor heart is placed into a recipient who is in need of a healthy heart.
- A heart-lung transplant is similar, but when both heart and lungs are transplanted into a recipient in the same procedure.
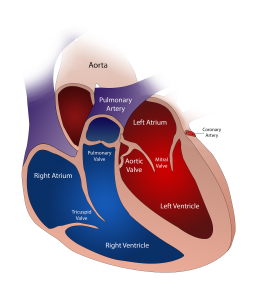
Heart Valve Replacement
- Some people are either born with or develop injury to one (or more) of the four valves in the heart. Valves help to control normal blood flow throughout the heart. Depending on the type and extent of injury or condition of the valve, surgical repair or replacement may be indicated. The type of surgery (whether it is open heart surgery or something less invasive) will depend on the extent of injury.
Pacemaker Implant
- A pacemaker can be surgically implanted in patients who have heart conditions regarding a slow, fast or irregular rhythm. Pacemakers deliver impulses to the heart to help it beat normally.