The most common medical problem in the world is back pain. Back pain can be dull, constant, sharp, or sudden. It can occur suddenly—as a result of a fall or lifting heavy objects—or it may be a continuous problem due to old age or an old injury. Whatever be the reason, back pains can be a real problem to anyone suffering with it.
Risk factors
Anyone can have back pain, young or old, but there are risk factors which increases your chances of getting a back pain. These factors include:
• Heredity — Diseases like ankylosing spondylitis is a heredity disease, that is passed on through the genes of prior generations.
• Age — With age, the degenerative process occurs in bones. Back pain usually starts at ages 30 to 40 and the number of occurrences gradually increases with increasing age.
• Diet — An improper diet, that is, high-calorie and high-fat diet causes obesity. The extra body weight puts a lot of stress on the back causing back pain.
• Physical fitness — Back pain is more prominent among people with lower fitness levels. Weak back muscles are not able to support the spine and leads to back pain. People who don’t exercise regularly or exert themselves one day after being inactive for a long period of time, is the cause of many back injuries.
• Occupation — The occupation of some people may entail them to do pushing, pulling, or heavy lifting. These activities can lead to injuries of the back and severe back pain. Sedentary jobs, especially with improper posture or uncomfortable chairs, can also cause back pains.
• Smoking — Smoking does not directly cause back pain, but it increases your risks. Coughing due to heavy smoking can cause back pain. Osteoporosis is a physical condition where the bones become weak and porous and lead to back pain. Smoking can cause osteoporosis. Smoking can delay the healing process of a back injury by blocking nutrients to the affected area.
Causes
Back pain is not a medical condition; rather, it is a symptom of some other medical condition. Back pain can be caused due to one or more of the following conditions:
Injury
Injuries like sprains, that is, tearing of the ligaments of the spine can cause back pain. Even fractures of the spinal vertebrae, the bones of spine can cause back pain too. Injuries can also be due to falls.
Medical Conditions
There are many medical problems involving the spine and the surrounding muscles, ligaments, and tissues that cause back pain. Some of the pains are caused due to prolonged diseases while others are due to a recent medical problem. Some of the medical problems which cause back pain are listed below:
- Degeneration of the intervertebral disk: Due to age, the disks between the vertebrae break down and lose the cushioning effect and thereby causes friction between the vertebrae.
- Herniated or ruptured disk: When the intervertebral disks become too weak, their outer ring tears and bulges out. The bulge causes pressure on the nearby spinal nerves.
- Osteomyelitis and diskitis: Osteomyelitis is an infection of the vertebrae while diskitis is the infection of the disks.
- Arthritis: All types of arthritis—osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, as well as spinal stenosis, which is the narrowing of the spinal cord—causes pain in the back.
- Scoliosis: An abnormal curvature of the spine, which causes problem in middle age and later.
- Osteoporosis: This causes the bones to become porous and weak and in turn causes vertebrae to fracture.
- Tumors due to cancer: Though rare, cancers in different parts of the body can cause tumors at the back, which puts pressure on the nerves of the back.
- Other causes: The other medical issues can include, pregnancy, fibromyalgia (muscle pain and fatigue), and endometriosis (a condition where the uterine tissue is found elsewhere in the body).
Stress
Emotional stress can affect the physical condition of the body. It can make the back muscles tight, stiff and painful. It can also affect the severity and duration of the pain.
Prevention
Exercise is one of the best methods of preventing back pain. Strengthening exercises make the muscles that support the back strong. Strong muscles also increases balance and decreases the risk of falling—preventing fractures, injuries, and pain.
Maintaining good posture and using proper back support can go a long way in avoiding stress on your back. Heavy lifting should be avoided or objects should be lifted with proper mechanics—lifting while keeping the object close to the body, backs should be kept straight, and lifting should be done using the legs and knees and not the muscles of the back.
Diet is another major way to prevent back pain. Firstly, a balanced diet should be eaten to maintain a healthy body weight. Back pain is more prominent in people who are overweight due to excess pressure on the back muscles. Getting the right amounts of calcium and vitamin D should be included in your diet to prevent osteoporosis and other bone diseases.
When and who you should see in case of back pain
 In the early stages, most back pain can be treated with medicine and rest. However, if the pain is severe, or it’s associated with weakness, numbness, fever, weight loss, or problems with urination; it can be serious. It’s better to seek medical advice for severe back pain. An initial checkup is usually done by your regular doctor and if possible, your doctor will treatment the pain or refer you to a specialist, like neurologist or orthopedist.
In the early stages, most back pain can be treated with medicine and rest. However, if the pain is severe, or it’s associated with weakness, numbness, fever, weight loss, or problems with urination; it can be serious. It’s better to seek medical advice for severe back pain. An initial checkup is usually done by your regular doctor and if possible, your doctor will treatment the pain or refer you to a specialist, like neurologist or orthopedist.
Diagnosis
The initial diagnosis involves a complete history and physical examination. During the history, your doctor asks questions on the nature of the pain, the severity, when it hurts, and where. On physical examination, the doctor checks your gait, your reflexes, muscle strengths, signs of nerve root irritation, and also tender points if any.
Depending on the history and physical, the doctor will decide if additional tests are required. If required, your doctor may order one or more of the following tests to confirm the diagnosis:
Xrays — are done to get pictures of bones or bony structures of your back. An xray is usually ordered if the doctor suspects osteoarthritis, fracture, or improper alignment of the spine.
MRI — Magnetic resonance imaging is a technique where, unlike x-rays, we can get clear pictures of not only the bones but also of the soft tissues like ligaments, tendons, and blood vessels. The doctor orders an MRI if he suspects infection, tumor, inflammation, or pressure on a nerve. An MRI is usually ordered if the pain does not subside after three to six weeks.
CT scan — Computed tomography scan is the process where two-dimensional pictures are transformed into three-dimensional pictures, which gives a better view of the spinal structures. A CT scan is ordered to check for herniated disks, tumors, or spinal stenosis.
Blood tests — Though rare, doctors may order blood tests such as a CBC, sedimentation rate, CRP, and HLA-B27.
Treatment options
Most acute back pains get better with time, regular activities and avoiding heavy exercises, while some may require anti-inflammatory medications like aspirin, ibuprofen, or acetaminophen. However, more serious back pains can be treated in two ways – surgery or other nonsurgical methods.
Nonsurgical Treatment options
Exercise — Exercises if done correctly can reduce a lot of chronic back pains. Exercises like flexion, extension, stretching, and aerobics not only rectify certain specific back pains but also help in the overall fitness of the body.
Medication — Some of the medications required to treat chronic back pain are easily available over the counter while the others require a prescription. Medications that are commonly used are analgesics like acetaminophen, aspirin, oxycodone, hydrocodone; NSAIDs like ibuprofen, ketoprofen, naproxen sodium, muscle relaxants and antidepressants. Topical analgesic products like Icy Hot, Zostrix, or Bengay are also prescribed to ease the pain. However, all these should be used under the supervision of your doctor as these might have side effects or interact with other medicines you are taking. For example, NSAIDs are known to cause side effects ranging from stomach discomfort to kidney dysfunction.
Traction — This method uses pulleys and weights to stretch the muscles and take pressure off the disks. The bones are pulled which increases the spaces between the vertebrae and brings temporary relief. It might be helpful in cases of slipped disk, where the pulling might cause the disk to settle back in its place.
Hot/cold packs — Hot or cold packs or even a combination of both are used in chronic back pains. Though they are not able to heal the actual cause of the pain, they can relieve the pain itself considerably. Heat causes the blood vessels to expand and hence carry more oxygen to the back. This reduces muscle spasms and also alters the feeling of pain. Cold on the other hand contracts the blood vessels and hence less blood flows to the back, which helps in reducing inflammation. It also makes the area numb due to which one does not feel the pain.
Braces — Braces along with corsets, elastic bands, and other stiff support and metal devices help in giving support, maintaining correct posture, and limiting motion. Though these may not cure the actual cause of the pain, but they can definitely help in the healing process, more so after surgery.
Injections — When the above mentioned medications and other methods do not work, injections are prescribed by the doctor. These include nerve root blocks, facet joint injections, trigger point injections, or prolotherapy – a method of injecting sugar solution on the covering of the bone to induce tissue growth which will strengthen the ligaments and tendons.
TENS — Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation is a method of sending mild electrical impulses to the nerves in the particular area using an electrical stimulator attached to the body. The mild electrical impulses cause the nerves to stop sending pain signals to the brain.
Acupressure — This is an ancient Chinese technique where pressure is applied by fingers on certain points on the body in order to activate the body’s self-healing abilities. When pressure is applied on these points, the muscle becomes tense, which in turn increases the blood circulation and helps the healing process.
Acupuncture — This is similar to acupressure except that needles are inserted at the pressure points instead of pressing with fingers.
Rolfing — This is a type of massage done by applying strong pressure on the fascia, which is the layer of tissue covering the muscles. The release of fascia from the muscle and tissues helps the back to return to its former self, and relieve pain.
Surgical Treatment Options
Surgery is required when the injury is severe or if the patient is suffering from chronic back pain and none of the conservative or nonsurgical treatments worked. A patient maybe considered to be a candidate for surgery, if he or she is having constant pain, which is causing problem with his or her profession or activities of daily living. However, there are various types of surgeries that are done depending on the condition or nature of the problem. Some of the surgeries are listed below.
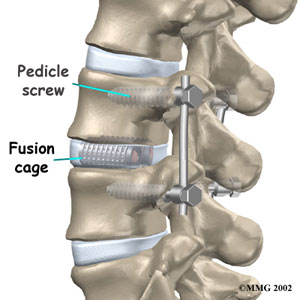 Spinal fusion— In this procedure a segment of two vertebrae are fixed together with screws, rods, and grafts so that particular segment becomes immobilized. This is usually done in patients suffering from either recurrent herniated disk, instability, spinal stenosis, or spondylolisthesis. In spondylolisthesis, the extra bony growths are removed before fusion of the vertebrae.
Spinal fusion— In this procedure a segment of two vertebrae are fixed together with screws, rods, and grafts so that particular segment becomes immobilized. This is usually done in patients suffering from either recurrent herniated disk, instability, spinal stenosis, or spondylolisthesis. In spondylolisthesis, the extra bony growths are removed before fusion of the vertebrae.
Disk replacement — In this procedure, the disk that is herniated is removed and an artificial disk is put in its place. This helps in the functioning of the segment. Replacement is used as an alternative to diskectomy where the disk is just removed. Disk procedures are done to correct degenerative disk disease.
IDET — Intradiskal electrothermal therapy is a newer procedure used to treat degenerative disk disease. In IDET, a small incision is made at the back and a heating wire is inserted through it to pass electrical current. This current strengthens the collagen fibers which hold the disks together.
Vertebroplasty — This procedure is used for vertebral fractures caused either by injury or osteoporosis. A mild incision is made at the fracture site with injection of polymethylacrylate through it in order to cement the fracture and stabilize the spine.
Kyphoplasty — Also known as balloon kyphoplasty is similar to vertebroplasty and is used as an alternative to treat fractures. In this procedure, a balloon is inserted through a needle into the fractured vertebra and inflated to create a cavity. The cavity is then filled with polymethylacrylate to cement the two bones together.
Laminectomy — This procedure is used to treat herniated disks or spinal stenosis. A large incision is made to open the spine and release the pressure by removing a portion of the vertebra—the lamina—and/or any osteophytes or bony growth. In case of herniated disk, the disk is also removed. Since this is a major surgery, it should be followed by physical therapy to regain back the strength and normal function.
Microdiskectomy — Similar to diskectomy, this surgery is used for removal of the herniated disk or portions of a damaged disk. It requires a much smaller incision. Additionally, a magnifying microscope or lens is inserted through the incision to locate the disk and assist in the removal.
Laser surgery — This is the latest form of surgery used for those suffering from herniated disks. This procedure involves insertion of a needle into the herniated portion and passing laser energy through it. The laser energy vaporizes the disk tissues reducing its size relieving the pressure on the spinal nerves.